Pillars of Object Oriented Programming
Pillars of Object Oriented Programming
The features which make the language ‘Object Oriented Language’, are called the Pillars of Object Oriented Programming.
Major Pillars
1 Abstraction
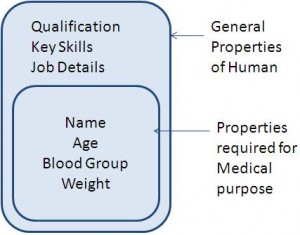
- Getting only essential things and hiding unnecessary details is called abstraction.
- It is the public access region of the class.
- Generally, it declares the operations that can be invoked by the clients on object of class.
- Avoid using data members in public region of class, as it may be directly changes by the client.
2 Encapsulation
- Binding of data and code together is called encapsulation.
- Encapsulation maintains integrity of object.
- For example, the Man class has a walk() method. The code for the Walk() method defines exactly how a walk happens.
- The encapsulation is most often achieved through information hiding.
- Information hiding is the process of hiding all the secrets of an object that do not contribute to its essential characteristics; typically,structure of an object is hidden, as well as implementation of its methods.
3 Modularity
- The act of portioning a program into individual components can reduce its complexity to some degree.
- Modularity can be physical modularity(e.g. divide program into .h, .cpp, .rc files) or logical modularity(e.g. namespace)
- Modularization consists of dividing program into modules that can be compiled seperately, but which are interconnected.
- Modularity helps in easier maintenance of a complex software.
4 Hierarchy
Hierarchy is ranking or ordering of abstractions.
Main purpose of hierarchy is to achieve re-usability.
The hierarchies are:
1. Inheritance (is-a relationship):
Acquiring all the properties(data members) and behaviors of one class by another class is called inheritance.
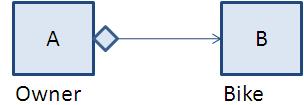
2. Composition (has-a relationship):
When object is madhe from other small objects it is called composition.
A is owner of B and B is non shareable.
3. Aggregation (has-a relationship):
A has B, A is owner of B, and B is shareable.
4. Aggregation (work-for relationship):
- Two objects works together for long time.
- It is bidirectional relationship
- In association, both are independent entities but just working together for long duration.
5. Dependency (use-a relationship):
- Sometimes the relationship between two classes is very weak.
- They are not implemented with member variables at all.
- Rather they might be implemented as member function arguments.
Polymorphism
It is Greek word which is a combination of poly(many) + morphism(forms/behavior).
One interface having many behaviors such phenomenon is called polymorphism.
Types of polymorphism:
1. Compile time polymorphism:
- It is also called as static polymorphism, false polymorphism, early binding.
- When call to functions is resolved at compile time it is called compile time polymorphism.
- In c++, Compile time polymorphism is achieved by using function overloading and operator overloading.
2. Run time polymorphism:
- It is also called as dynamic polymorphism, true polymorphism or late binding.
- When call to the function resolved at run time, it is called run time polymorphism.
- In c++, run time polymorphism is achieved by using function overriding.
Minor Pillars
1 Concurrency
- The concurrency problem arises when multiple threads simultaneously access same object.
- We may use a class library for providing threading support.
- We may use interrupts to give illusion of concurrency which need hardware details.
- You need to take care of object synchronization when concurrency is introduced in the system.
2 Persistence
- It is property by which object maintains its state across time and space.
- The concept gives rise to the concept of object oriented database.
- It talks about concept of serialization and also about transferring object across network.