Java default values
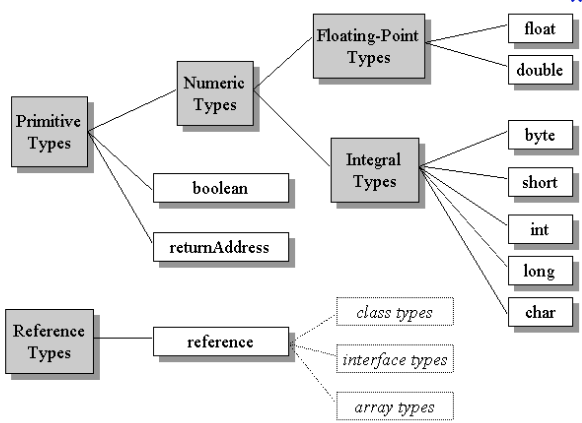
Default Value of Data Types in Java :
| Data Type | Default Value (for fields) |
|---|---|
| byte | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| long | 0L |
| float | 0.0f |
| double | 0.0d |
| char | ‘u0000’ |
| String (or any object) | null |
| boolean | false |
Live Example : Default value of Data Type
Sample Program that will illustrate Default Value Stored in Each Primitive Data Type Variable
public class DefaultValue { static boolean bool; static byte by; static char ch; static double d; static float f; static int i; static long l; static short sh; static String str; public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Bool :" + bool); System.out.println("Byte :" + by); System.out.println("Character:" + ch); System.out.println("Double :" + d); System.out.println("Float :" + f); System.out.println("Integer :" + i); System.out.println("Long :" + l); System.out.println("Short :" + sh); System.out.println("String :" + str); } }
Output :
[468×60]
Bool :false Byte :0 Character: Double :0.0 Float :0.0 Integer :0 Long :0 Short :0 String :null