Bitwise XOR : Bitwise Operators in Java Programming
Bitwise XOR Operator is -
- The XOR operator (^) combines bits such that if either of the bits in the operands is a 1, then the resultant bit is a 1
- Binary Operator as it Operates on 2 Operands.
- Denoted by : ^
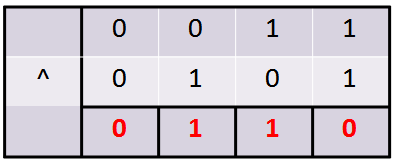
Bitwise XOR Summary Table :
| A | B | A ^ B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Live Example 1 : XORing 42 and 15
class BitwiseXOR { public static void main(String args[]){ int num1 = 42; int num2 = 15; System.out.println("XOR Result =" +(num1 ^ num2)); } }[468x60]
Output :
XOR Result = 37
Explanation of Code :
Num1 : 00101010 42 Num2 : 00001111 15 ====================== XOR : 00100101 37
- 42 is represented in Binary format as -> 00101010
- 15 is represented in Binary format as -> 00001111
- According to above rule (table) we get 00100101 as final structure.
- println method will print decimal equivalent of 00100101 and display it on screen.
Live Example 2 : ORing Hex and Integer
class BitwiseXOR { public static void main(String args[]){ int num1 = 42; int num2 = 0xF; System.out.println("XOR Result =" +(num1 ^ num2)); } }
- Code will also gives 37 as a result.
- 0xF is hexadecimal number.
- 0xF is first converted into “decimal“.(Decimal Equivalent : 15)
- Again Same Operation will takes place as that of “Live Example 1“.
Step 1: Converting Hex to Decimal Num2 : F (Hex) : 15 (Decimal Equivalent)
Step 2: Converting Decimal to Binary Num1 : 00101010 42 Num2 : 00001111 15 ====================== XOR : 00100101 37[468x60]
Bitwise Logical Operators : AND | OR | NOT | XOR
