Java If Statement
Contents
- 1 If Statement in Java Programming : Conditional Selection
- 2 Syntax : If Statement
- 3 Syntax : If-Else Statement
- 4 Syntax : If-Else Ladder Statement
- 5 Live Example 1 : Simple If-Else Ladder Statement
- 6 Output :
- 7 Live Example 2 : Simple If-Else Ladder Statement
- 8 Output :
- 9 Live Example 3 : Simple If-Else Ladder Statement
- 10 Output :
- 11 Live Example 4 : We can have multiple conditions inside If
- 12 Must Read Note :
- 13 Output :
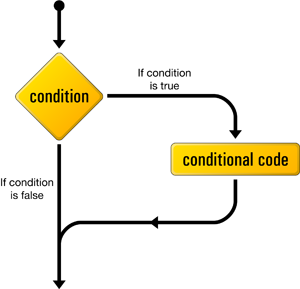
If Statement in Java Programming : Conditional Selection
- The if statement is a conditional branch statement.
- It tells your program to execute a certain section of code only if a particular test evaluates to true.
- If boolean Expression evaluates to true, the statements in the block following the if statement are executed.
- If it evaluates to false, the statements in the if block are not executed.
Syntax : If Statement
if (booleanExpression) { statement(s) }
- If boolean Expression evaluates to false and there is an else block, the statements in the else block are executed.
Syntax : If-Else Statement
if (booleanExpression) { statement(s) } else { statement(s) }
Syntax : If-Else Ladder Statement
- If we have multiple conditions then we can use if-else ladder -
if (booleanExpression1) { // statements } else if (booleanExpression2) { // statements } ... else { // statements }
Live Example 1 : Simple If-Else Ladder Statement
class IfDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int marks = 76; String grade; if (marks >= 40) { grade = "Pass"; } if (marks < 40) { grade = "Fail"; } System.out.println("Grade = " + grade); } }
Output :
Grade = PassLive Example 2 : Simple If-Else Ladder Statement
class IfDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int marks = 76; String grade; if (marks >= 40) { grade = "Pass"; } else { grade = "Fail"; } System.out.println("Grade = " + grade); } }
Output :
Grade = PassLive Example 3 : Simple If-Else Ladder Statement
class IfElseDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int marks = 76; char grade; if (marks >= 90) { grade = 'A'; } else if (marks >= 80) { grade = 'B'; } else if (marks >= 70) { grade = 'C'; } else if (marks >= 60) { grade = 'D'; } else { grade = 'F'; } System.out.println("Grade = " + grade); } }
Output :
Grade = CLive Example 4 : We can have multiple conditions inside If
if(marks > 70 || marks < 90) System.out.println("Class A"); else System.out.println("Class B");
- We can use “&&” , “||” operators in order to refine condition.
- && operator will check whether both left hand and right hand conditions are true or not.
- || condition will check
Must Read Note :
If we have written two conditions inside “If Condition” then -
- If First Condition is true then || operator will skip checking second condition.
- If First Condition is false then || operator will check second condition if second condition is true then overall if will follow true block otherwise it will follow else block.
Proof -
class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 20; if ((++num1 > 0) || (++num2 > 0)) { System.out.println(num1); System.out.println(num2); } } }
Output :
11 20
Explanation :
- First condition is true so it skip out checking second condition.
class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 20; if ((++num1 < 0) && (++num2 > 0)) { System.out.println(num1); System.out.println(num2); } System.out.println(num1); System.out.println(num2); } }
Output :
11 20
Explanation :
- If First Condition is true then && operator will check second condition.
- If First Condition is false then && operator will skip checking second condition.