Java HashMap : Collection Class
Java HashMap : Collection Class
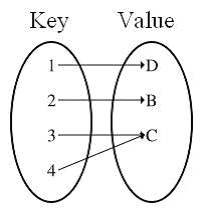
- HashMap class uses a hashtable to implement the Map interface
- HashMap is a data structure which works on hashing techniques.
- HashMap allows us to store the object as key-value pair.
- HashMap is used to retrieve the object in constant time O(1)
- HashMap implements the Map interface and extends AbstractMap class.
- HashMap can only contain unique keys.
- HashMap does not maintains any order.
Lets create an HashMap using following line of code -
Example #1 : Create HashMap
package com.c4learn.collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; public class HashMapExample { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String,String> hMap = new HashMap<String,String>(); hMap.put("A1", "Aman"); hMap.put("A2", "Arun"); hMap.put("A3", "Akash"); hMap.put("A4", "Aniket"); hMap.put("A5", "Anil"); Set set = hMap.entrySet(); Iterator itr = set.iterator(); while (itr.hasNext()) { Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) itr.next(); System.out.println(m.getKey() + " " + m.getValue()); } } }
Output :
A2 Arun A1 Aman A4 Aniket A3 Akash A5 Anil
Explanation :
Following line of code is used to create the HashMap in Java.
HashMap<String,String> hMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
Now if we need to add a pair of name & value to the map then we can use put method for adding element to the Map.
hMap.put("A1", "Aman"); hMap.put("A2", "Arun"); hMap.put("A3", "Akash"); hMap.put("A4", "Aniket"); hMap.put("A5", "Anil");
We have added 5 elements to the Map.