C register storage class
Register Storage Class :
- Register is used to define Local Variable.
- Local Variable stored in Register instead of RAM.
- As Variable is stored in Register so Maximum size of variable = Maximum Size of Register
- Unary Operator [&] is not associated with it because Value is not stored in RAM instead it is stored in Register.
- This is generally used for faster access.
- Common use is “Counter“
Syntax :
{
register int count;
}
Live Example : Register Storage Classes
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int num1,num2; register int sum; printf("\nEnter the Number 1 : "); scanf("%d",&num1); printf("\nEnter the Number 2 : "); scanf("%d",&num2); sum = num1 + num2; printf("\nSum of Numbers : %d",sum); return(0); }
Explanation of Above Code :
Refer below animation which depicts the register storage classes -
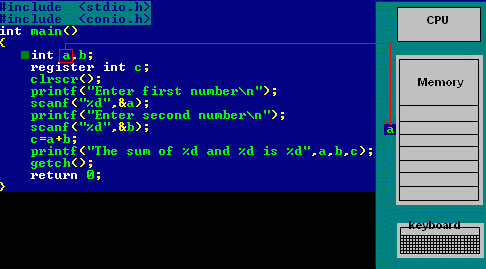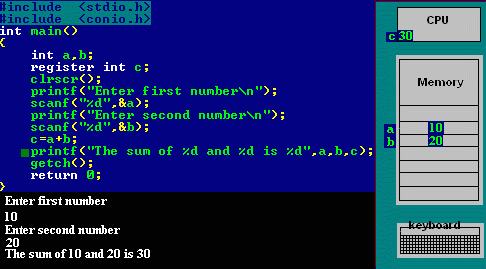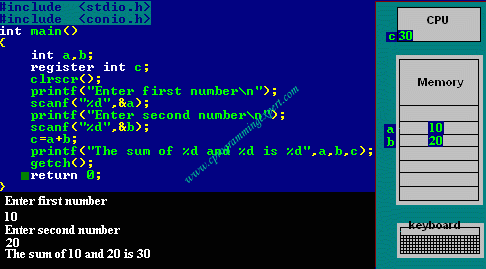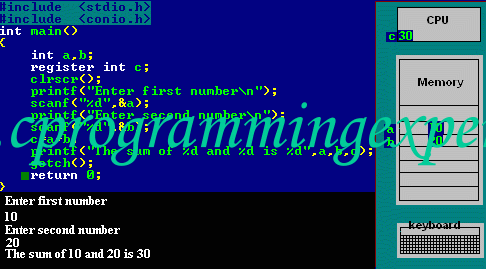
Reference : [cprogrammingexpert]
- In the above program we have declared two variables num1,num2. These two variables are stored in RAM.
- Another variable is declared which is stored in register variable.Register variables are stored in the register of the microprocessor.Thus memory access will be faster than other variables.
- If we try to declare more register variables then it can treat variables as Auto storage variables as memory of microprocessor is fixed and limited.
Summary of Register Storage Class in C :
| Keyword | register |
|---|---|
| Storage Location | CPU Register |
| Initial Value | Garbage |
| Life | Local to the block in which variable is declared. |
| Scope | Local to the block. |
Why we need Register Variable :
- Whenever we declare any variable inside C Program then memory will be randomly allocated at particular memory location.
- We have to keep track of that memory location. We need to access value at that memory location using ampersand operator/Address Operator i.e (&).
- If we store same variable in the register memory then we can access that memory location directly without using the Address operator.
- Register variable will be accessed faster than the normal variable thus increasing the operation and program execution. Generally we use register variable as Counter.
Note : It is not applicable for arrays, structures or pointers.
