C passing entire array to function
Passing entire array to function :
- Parameter Passing Scheme : Pass by Reference
- Pass name of array as function parameter .
- Name contains the base address i.e ( Address of 0th element )
- Array values are updated in function .
- Values are reflected inside main function also.
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> //--------------------------------- void fun(int arr[]) { int i; for(i=0;i< 5;i++) arr[i] = arr[i] + 10; } //-------------------------------- void main() { int arr[5],i; clrscr(); printf("\nEnter the array elements : "); for(i=0;i< 5;i++) scanf("%d",&arr[i]); printf("\nPassing entire array ....."); fun(arr); // Pass only name of array for(i=0;i< 5;i++) printf("\nAfter Function call a[%d] : %d",i,arr[i]); getch(); }
Output :
Enter the array elements : 1 2 3 4 5 Passing entire array ..... After Function call a[0] : 11 After Function call a[1] : 12 After Function call a[2] : 13 After Function call a[3] : 14 After Function call a[4] : 15
Graphical Flowchart :
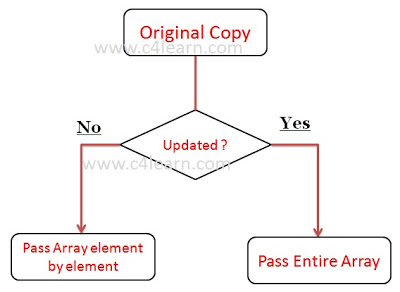
Passing Entire 1-D Array to Function in C Programming
- Array is passed to function Completely.
- Parameter Passing Method : Pass by Reference
- It is Also Called “Pass by Address“
- Original Copy is Passed to Function
- Function Body Can Modify Original Value.
- Example :
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void modify(int b[3]); void main() { int arr[3] = {1,2,3}; modify(arr); for(i=0;i<3;i++) printf("%d",arr[i]); getch(); } void modify(int a[3]) { int i; for(i=0;i<3;i++) a[i] = a[i]*a[i]; }
Output :
1 4 9
- Here “arr” is same as “a” because Base Address of Array “arr” is stored in Array “a”
Alternate Way of Writing Function Header :
void modify(int a[3])
OR
void modify(int *a)
